Kane County Monitors Air Quality to Protect Public Health — Here's Why It Matters
Kane County Monitors Air Quality to Protect Public Health — Here's Why It Matters
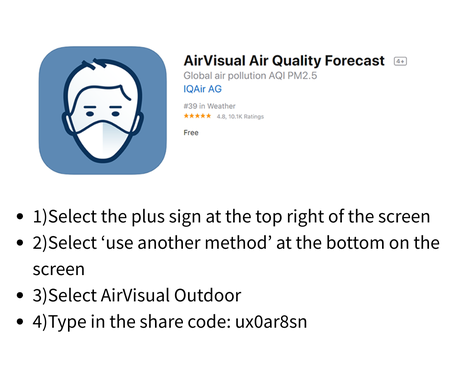
Kane County is taking proactive steps to protect the health and well-being of its residents by monitoring air quality at the Kane County Government Center (791 S. Batavia Ave.) in Geneva. With newly installed indoor and outdoor sensors, the County tracks key pollutants that can affect respiratory health and contribute to broader environmental challenges like climate change. Residents can view real-time outdoor air quality data here or download the AirVisual app to monitor conditions alongside the County (see instructions below).
Why It Matters
Air pollution, often invisible but always impactful, is a growing concern in Kane County and around the world. Whether caused by fine particulate matter from wildfire smoke or ozone formed on hot summer days, polluted air poses serious health risks. From 2020 to the present, Kane County's Air Quality Index (AQI) has ranged from 5 to 163. The highest levels were recorded in July 2023 and June 2025 due to smoke from the Canadian wildfires. With temperatures rising and drought conditions becoming more frequent, the risk of wildfires — and the harmful smoke they generate — is expected to increase in the coming years. 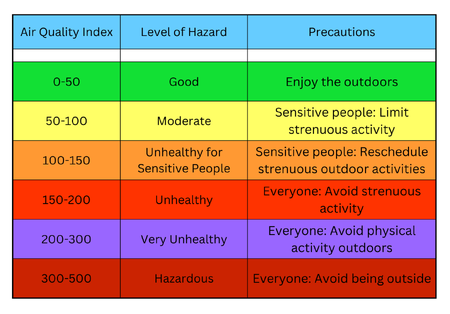
Air pollution is defined by the presence of one or more contaminants in the atmosphere, such as dust, fumes, gas, mist, odor, smoke, or vapor. These pollutants come from a variety of sources and often include ozone, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particles from inorganic compounds, soil, dust, pollen, or mold spores. While natural events like dust storms and wildfires contribute to air pollution, the majority of pollutants are linked to human activities — particularly the burning of fossil fuels for heating, transportation, and manufacturing.
Particulate matter, especially particles smaller than 10 micrometers in diameter (PM₁₀), poses significant health risks because it bypasses the body's natural defenses and enters the lungs. Short-term exposure is associated with reduced lung function, respiratory problems, aggravated asthma, coughing, and shortness of breath. In contrast, long-term exposure can lead to severe health impacts, including heart disease, stroke, chronic bronchitis, lung cancer, pregnancy complications, and cognitive impairment. The World Health Organization estimated in 2019 that 4.2 million people died prematurely due to air pollution. Among those deaths, 68% were attributed to heart disease and stroke, 14% to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, another 14% to acute lower respiratory infections, and 4% to lung cancer.
Major Air Pollutants and Their Sources
To better understand air pollution, it is important to recognize the major pollutants and where they come from.
- Ground-level ozone forms when nitrogen oxides and VOCs react with sunlight.
- Particle pollution (PM) consists of acids (such as sulfuric acid), inorganic compounds (like ammonium nitrate), organic chemicals, soot, metals, soil or dust particles, and biological materials. Although particle pollution is present everywhere, it is typically more concentrated in smoky, sooty, or dusty environments, especially in densely populated areas with significant manufacturing activity and vehicle traffic.
- Carbon monoxide is emitted by vehicles, power plants, wildfires, and household appliances that burn fuel.
- Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide are primarily produced by burning coal, oil, and natural gas. These gases react with other chemicals in the atmosphere to form fine particulate matter, which makes up the majority of fine particles in the United States.

What Residents Can Do — At Home and In the Community
Fortunately, there are several practical steps residents can take to protect themselves and reduce air pollution.At home, using low-VOC products and ensuring proper ventilation when painting or using chemicals can make a difference. Installing high-efficiency (MERV-rated) furnace filters and considering HEPA air purifiers also helps reduce indoor air pollutants. Weatherizing homes to prevent pollutants from entering and to reduce energy use is another effective strategy.
Energy conservation is equally important. Residents can reduce energy consumption by using Energy Star-rated appliances and installing smart thermostats. When upgrading heating and cooling systems, considering heat pumps, can offer long-term energy and cost savings.
In the community, residents can limit driving when possible, reduce vehicle idling, and opt for electric vehicles (which may qualify for a $7500 tax credit) or electric lawn equipment. Volunteering with local organizations, such as the Kane County Forest Preserve or the Chicago Region Tree Initiative, supports environmental restoration and helps improve air quality for everyone.
By understanding air pollution and taking simple steps to reduce exposure, residents can protect their health while contributing to the well-being of the entire community.
For more information, visit the Kane County Air Quality website and the Kane County Health Department for additional tips and resources.